How Are Proteins Changed To Become Recombinant Proteins?
Proteins are the workhorse in biological systems facilitating most of biological processes in a jail cell, including gene expression, cell growth, proliferation, nutrient uptake, intercellular advice and apoptosis. The bluish impress for poly peptide synthesis is stored in Deoxyribonucleic acid, which serves equally a template for highly regulated transcriptional processes to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). The message coded by mRNA is then translated into defined sequences of amino acids that form a poly peptide. Proteins are synthesized in a similar ii-step procedure in all organisms – DNA is starting time transcribed into RNA, then RNA is translated into protein.
What are recombinant proteins?
Recombinant proteins are proteins encoded past recombinant DNA that has been cloned in an expression vector that supports expression of the cistron and translation of messenger RNA. Modification of the gene past recombinant Dna engineering tin atomic number 82 to expression of a mutant protein. Recombinant poly peptide is a manipulated form of native poly peptide, which is generated in diverse means in social club to increment production of proteins, modify factor sequences, and industry useful commercial products.
How are recombinant proteins made?
Recombinant protein production begins at the genetic level, where coding sequence for the protein of interest is get-go isolated and cloned into an expression plasmid vector. Most recombinant proteins for therapeutic use are from humans just are expressed in microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, or animal cells in civilisation. Man genes are very circuitous, oft containing non-coding DNA sequences known as introns. Therefore, an intron-costless version of the cistron is often made past converting the mRNA into cDNA. Because the cDNA lacks regulatory regions, the expression vectors provide promoter, ribosome-binding site, and terminator sequences. Recombinant protein product for inquiry purposes is mainly driven by the cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and speed of the process in conjunction with adequate yields of the product. Proteins co-expressed in bacteria would not possess post-translational modifications, eastward.1000. phosphorylation or glycosylation; eukaryotic expression systems are needed for this.
Many recombinant proteins require protein modifications, such equally glycosylation, that are available simply in eukaryotic cells. Yeast, insect cells, and mammalian cell culture systems offer such post-translation modifications. Over the past decade, efficient transient transfection protocols take reportedly been developed. HEK293-derived cell lines are employed for transient production of proteins. Currently, most recombinant therapeutic proteins are produced in mammalian cells because mammalian cells are capable of producing high-quality proteins similar to the naturally occurring ones. In addition, many approved recombinant therapeutic proteins are generated in E.coli due to its well-characterized genetics, rapid growth, and high-yield production.
What are recombinant proteins used for?
Biomedical research to understand wellness and disease
Recombinant proteins are useful tools in agreement protein-protein interactions. Poly peptide interactions are fundamentally characterized as stable or transient and play an important role in cellular processes. Recently, RP microarrays for examining protein-protein interactions take become popular. For this arroyo, researchers seed a slide with numerous immobilized proteins, which they then treat with a diverseness of molecules to examine how the two agents interact with one another. Using this system, scientists take studied protein interactions with other proteins or peptides, enzymes, minor molecules, lipids, and nucleic acids. This allows for much higher throughputs when it comes to studying poly peptide-protein interactions.
Recombinant proteins have proven performance in several laboratory technique, such every bit ELISA, western blot and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Recombinant poly peptide are used to develop enzymatic assays. When used in conjunction with a matched antibody pair, recombinant proteins can be used every bit standards in ELISA, and equally positive controls in western blots, and IHC. Recombinant proteins serve every bit valuable tools for investigating cellular response to stress, and affliction situations. Recombinant proteins and peptides administered to animal models of disease aid researchers in identifying novel potential therapeutic candidates.
Recombinant proteins for biotherapeutics
Most human diseases are systemically or partially related to dysfunction of specific proteins. Therapeutic proteins provide important therapies for a multifariousness of diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, infectious diseases, hemophilia, and anemia. Common therapeutic proteins include antibodies, Fc fusion proteins, hormones, interleukins, enzymes, and anticoagulants. Homo proteins obtained through genetic engineering play a key role in therapeutic medicines market place. I of the many RP vaccines canonical past the FDA is the Hepatitis B vaccine for prevention of infection acquired by all known subtypes of the Hepatitis B virus.
The first recombinant poly peptide used in treatment was recombinant human insulin in 1982 and the RP industry has rapidly grown since. To date, more than 130 RPs have been approved by the The states FDA for clinical use. However, more than 170 RPs are produced and used in medicine worldwide. Recombinant human being insulin was a very early example of the use of biotechnology in drug development. Recombinant proteins are potent medicines that are safety from off-target side effects, and have a shorter time to develop than small-scale molecules. All Big Pharma now develop RP as drugs and thus, information technology is a multibillion dollar industry.
Recombinant proteins used in the clinic include recombinant hormones, interferons, interleukins, growth factors, tumor necrosis factors, blood clotting factors, thrombolytic drugs, and enzymes for treating major diseases such as diabetes, dwarfism, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cerebral occlusion, multiple sclerosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, Crohn'south disease, and cancers therapies. Backed by numerous peer-reviewed citations, Enzo offers an extensive range of recombinant and native proteins for a variety of research fields. Our proteins are validated in specific functional assays and are manufactured to the highest stringent quality.
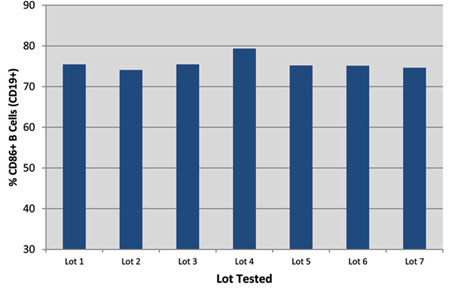 |
| Figure one: Figure i. Reliable manufacturing yields consistent results. MEGACD40L Poly peptide from 7 consecutive manufacturing lots were tested using B-cell activation assay at g ng/ml. |
Recombinant proteins are used in nutrient production, agronomics, and bioengineering. For example, in the breeding industry, enzymes can be added to beast feed to increase the nutritional value of feed ingredients, reduce feed and waste management costs, support beast gut wellness, enhance animal operation and improve the surround. Additionally, lactic acrid leaner (LAB) have been used for a long fourth dimension for the production of fermented foods. Recently, LAB has been engineered for the expression of recombinant proteins, which will have a wide range of applications such as improving homo/animate being digestion and diet.
Advancements in the field of biotechnology have increased and facilitated the production of recombinant proteins for various applications. The importance of RP has increased rapidly for basic life science enquiry, diagnostic reagents and therapeutic drugs. Their office in biotechnology is irreplaceable. Nosotros also look forward to seeing more progress in the treatment of diverse diseases with recombinant proteins. Enzo's catalog of widely cited and thoroughly validated native and recombinant proteins will help accelerate this research. Our decades of experience in the design and manufacturing of active enzymes, and drug discovery kits offers tools to screen inhibitors of specific enzymes and identification of a potential therapeutic target. Delight contact our Technical Support Team for further assistance.
Source: https://www.enzolifesciences.com/science-center/technotes/2020/january/why-do-we-need-recombinant-proteins?/
Posted by: wilsonmarmyre.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Are Proteins Changed To Become Recombinant Proteins?"
Post a Comment